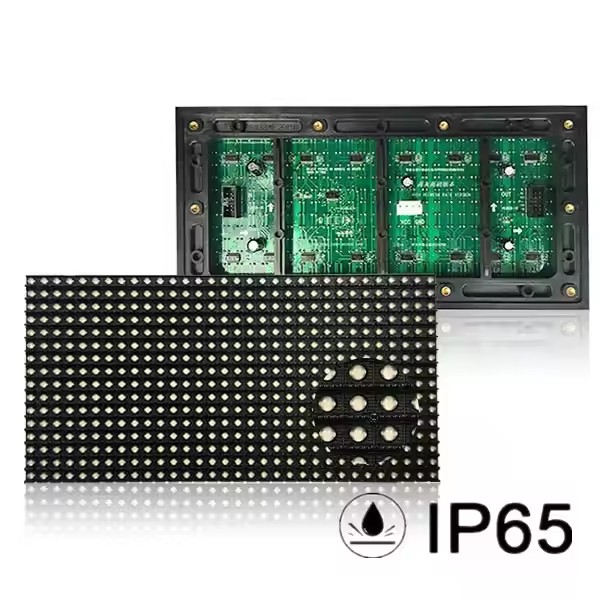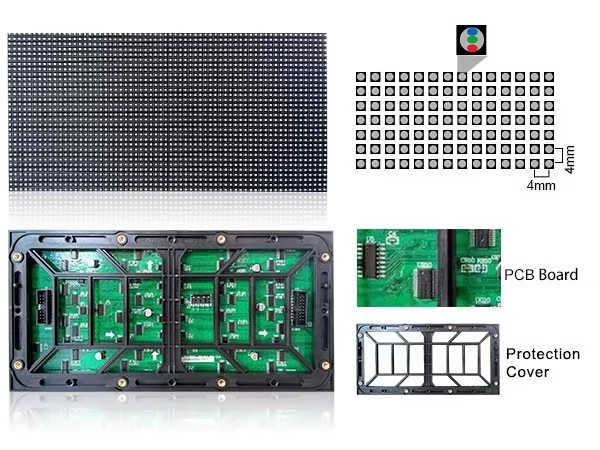
Working principle of LED module
LED module is the core display component of LED screen, which can display different color images. So at this time you may have questions, how does the LED module display colors? How does it work? In order to solve these questions, this article will take you to understand!
LED module light-emitting principle
LED modules mainly rely on LEDs (light emitting diodes) to emit light. The component material of LEDs is aluminum gallium arsenide (AlGaAs), which is a semiconductor material in which the atoms of the semiconductor material are close to each other.
It is usually not a pure material, but a semiconductor material in which the atoms of the semiconductor material are close to each other. This material is usually not pure, but doped with some other elements. This adds free electrons, or allows holes to be created between the electrons so that they can move freely.
These extra doped semiconductor materials are categorized into two types, N-type materials that have extra electrons and P-type materials that have holes.
N-type materials move free electrons from negatively charged regions to positively charged regions, while P-type materials are positively charged particles that jump electrons from one hole to another, bringing electrons from negatively charged regions to positively charged regions.
LEDs need to be bonded by a section of N-type material and P-type material with a positive and negative electrode applied to each end. This design structure allows the electrons to conduct in only one direction.
When the diode is not energized, the electrons in the N-type material fill the holes in the P-type material along the joint between the two layers and form a depletion region.
Within this depletion region, all the semiconductor material returns to its original state. The material in this state is in an insulating state at this point, and all the holes in the semiconductor material in this state will be filled, and the electrons at this point have lost their free state and are unable to move.
When we want the electrons to move freely again, we need to apply a voltage to the LED bead to reactivate the N-type material, whose free electrons are repelled by the negative electrons, allowing it to move towards the positive region. The P-type material at the other end moves in the opposite direction.
At the end of this process, all the electrons in the depletion region will be gone, and the electrons will leap from the higher energy orbitals to the lower energy orbitals above. In this process of leaping, the excess energy will be released in the form of photons all, so that the LED lamp beads produce light energy, so that the LED lamp beads to realize the independent light.

Color rendering principle of LED module
For LED module, it integrates LED beads of three different colors, red, green and blue, into one LED chip. Through the control system to control the LED chip, so that the three different colors of the LED lamp beads produce different brightness, so that their different wavelengths are superimposed together to form a different color spectrum, which in turn allows the LED chip to ultimately present the color of the spectrum of colors consistent with the color of the LED module can bring colorful display screen.

If the brightness of the three colors of LED beads is the same, then the wavelengths of the three colors of LED beads will be superimposed together to produce a white spectrum, which makes the final color emitted by the LED chip is white.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the reason why LED modules emit light is that LED beads can emit light on their own and produce different colors by mixing the three primary colors of light sources with different brightness, which makes the LED module able to present a full-color picture.
